The key to making a photon pulse (and avoid long wave train)
Problem: Every resonant circuit (tuning circuit, impedance change) collapses the electron wave function and transfers energy into a new wave function. This consumes time with multiple reflections as a signal is processed by one circuit after another. A single pulse is turned into a multiple pulse train by the resonating radio circuits.
光子パルスを作り長波長列を回避する仕組み
課題:すべての共振回路(同調回路、インピーダンスの変化)は、電子の波動関数を崩壊させ、新しい波動関数にエネルギーを伝達する。信号が次から次へと回路で処理され、多重反射によって時間が消費される。 単一のパルスは、共振する無線回路によって複数のパルス列に変わる。
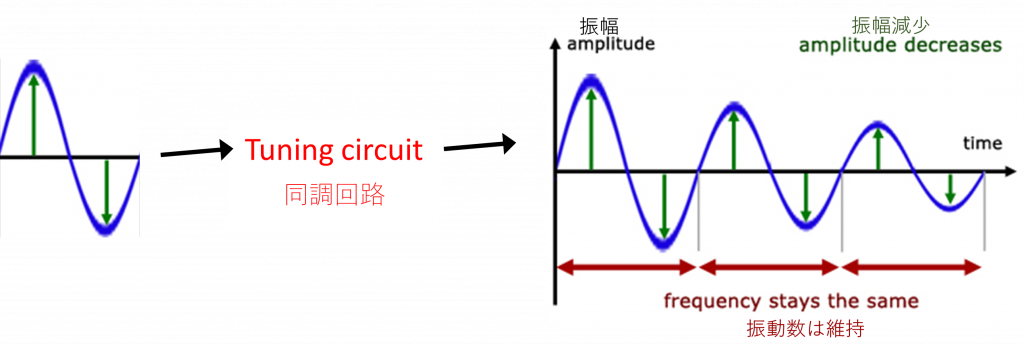
Solution: Eliminate resonance circuit hysteresis in the transmitter.
解決策:送信機の共振回路のヒステリシスをなくす。
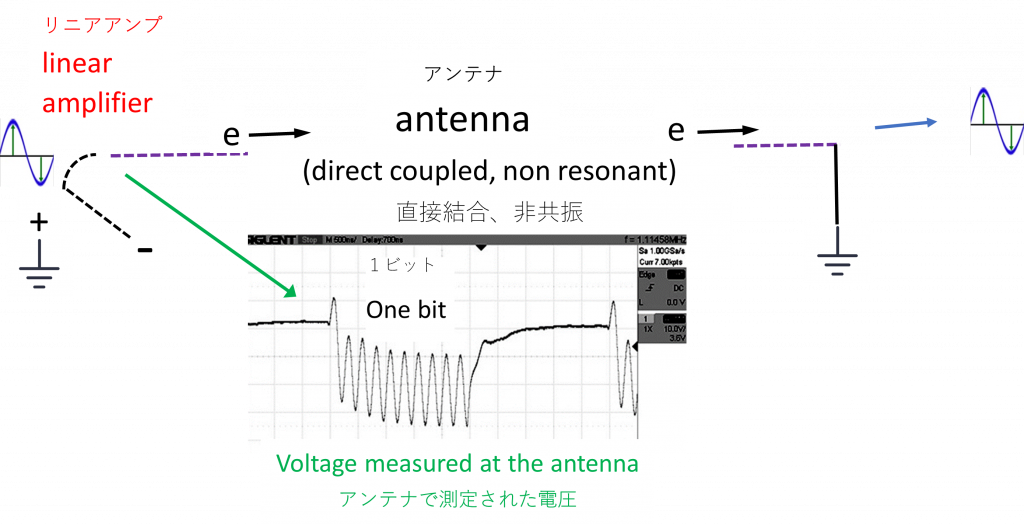
Our transmitter eliminates resonance.
(we avoid wave function collapse from reflections)
We send a direct current non reflective pulse
into a non-resonant antenna to transmit the short pulse.
私たちの送信機は共振を排除する
(反射による波動関数の崩壊を避ける)。
直流無反射パルスを無共振アンテナに送り、短パルスを送信する。
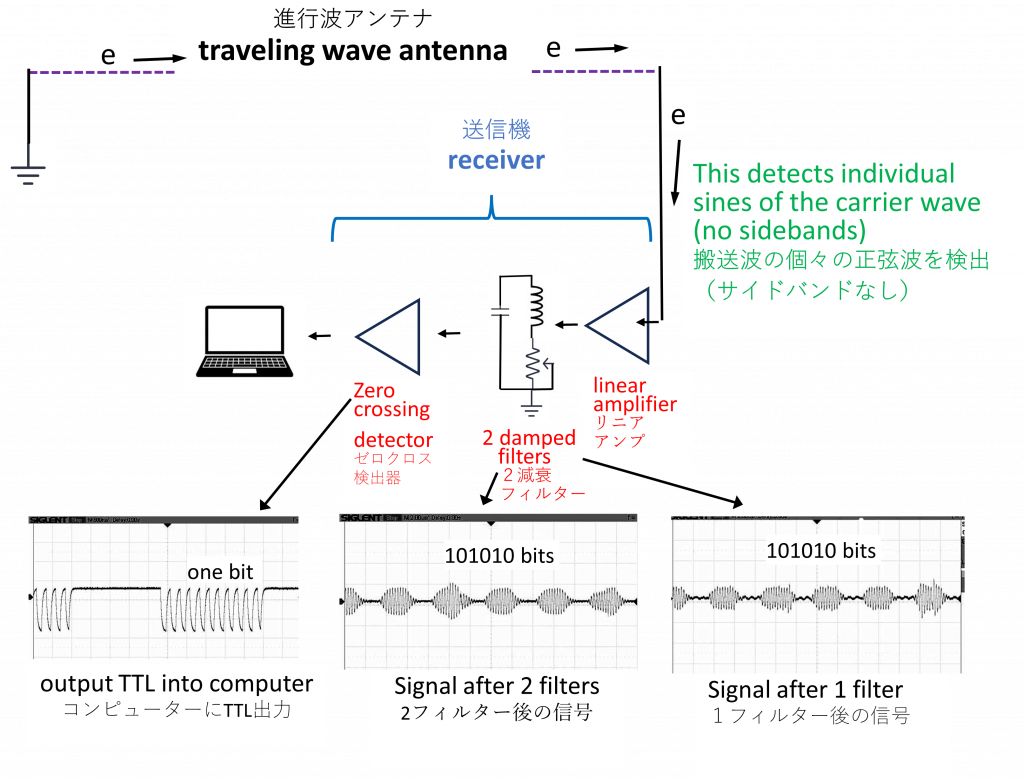
We use 2 to 10 photon pulses per bit to allow receiver tuning.
This is an example of 10 pulses per bit.
1. Minimize resonance in the receiver
2. Detect photon pulses with a zero crossing detector
受信機のチューニングを可能にするため、1ビットあたり2~10個の光子パルスを使用する。
これは1ビットあたり10個のパルスの例である。
1. レシーバーの共振を最小化
2. ゼロ交差検出器による光子パルスの検出